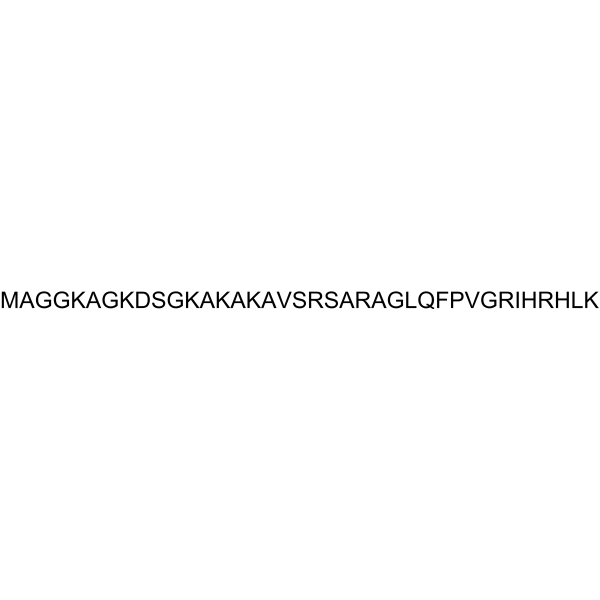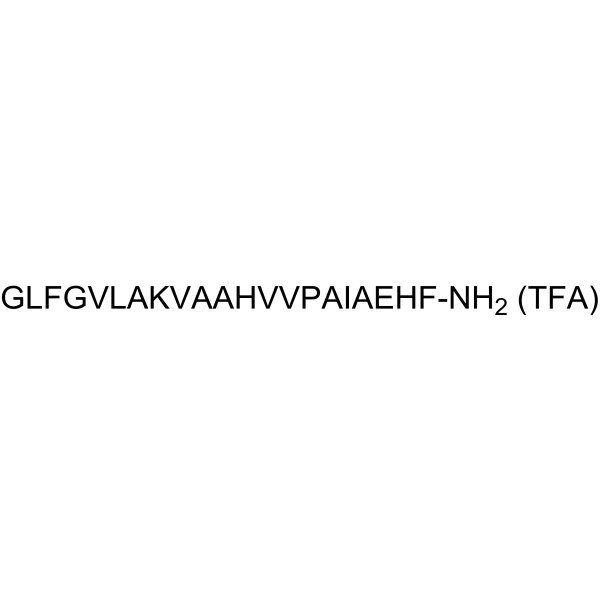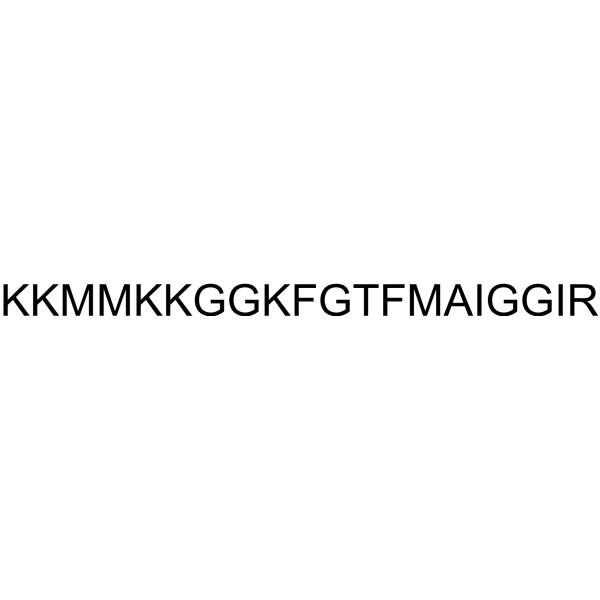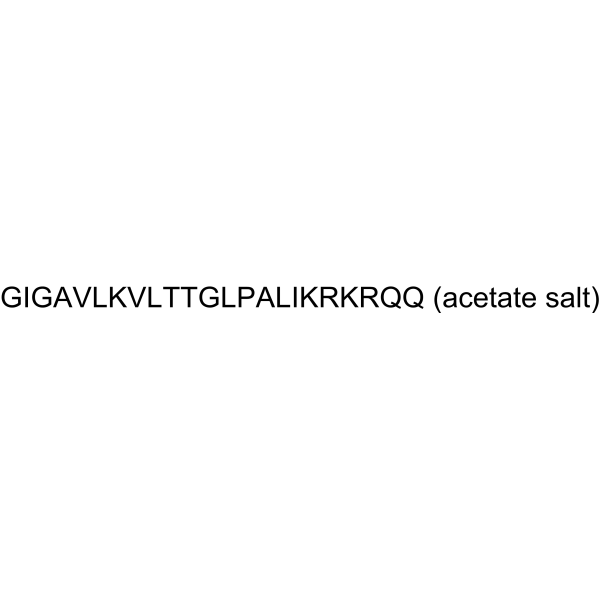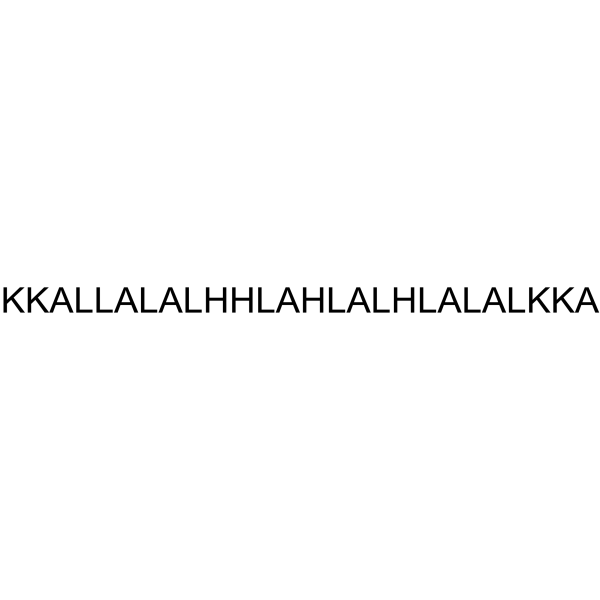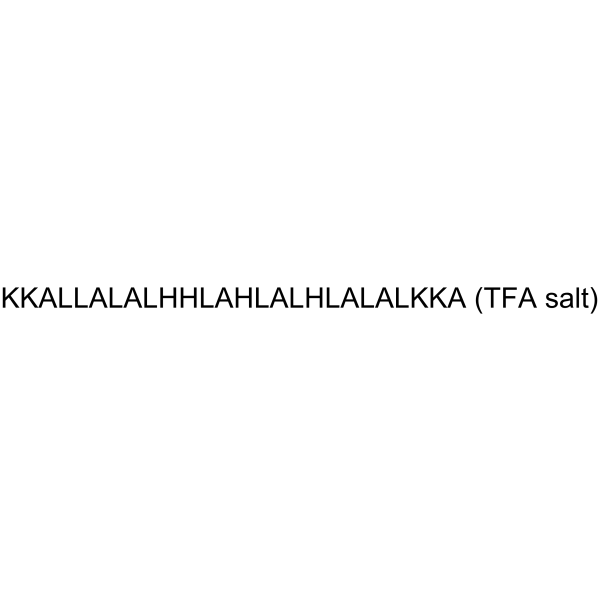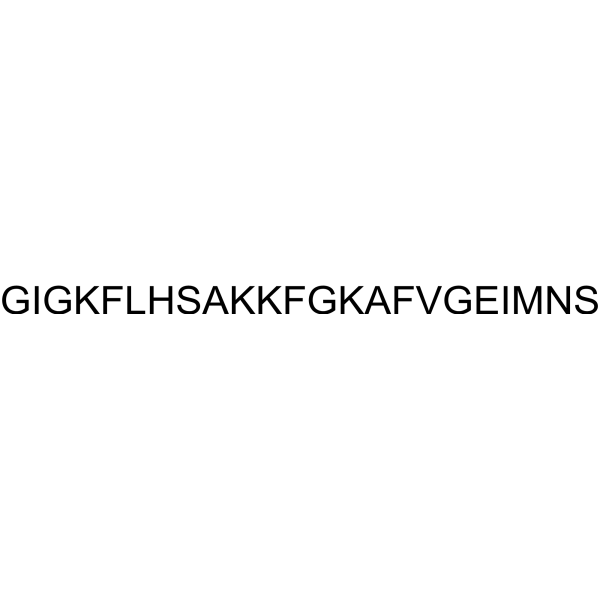Search Result
Results for "
Bacterial membrane
" in MedChemExpress (MCE) Product Catalog:
3
Biochemical Assay Reagents
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Areas |
Chemical Structure |
-
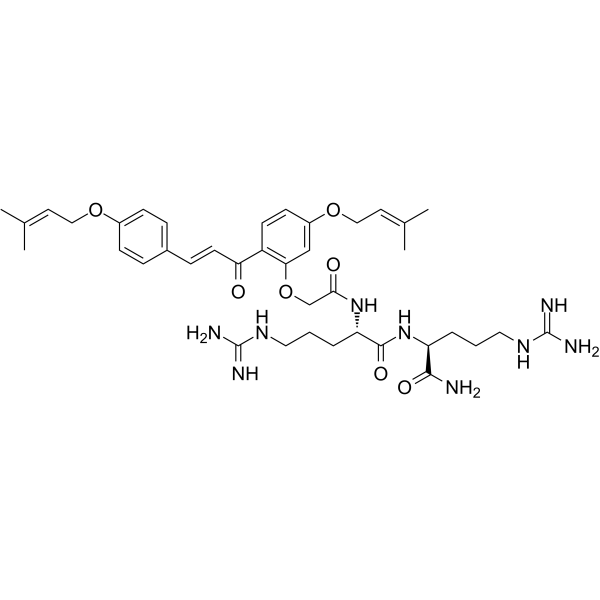
- HY-142991
-
-
-
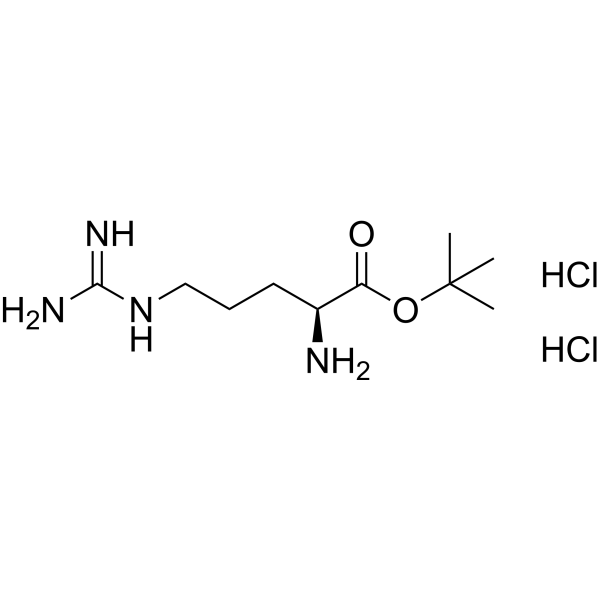
- HY-144823
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
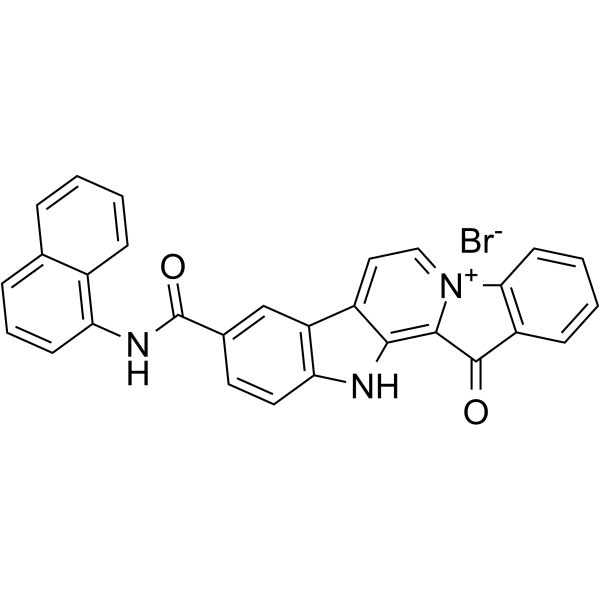
Anti-MRSA agent 3 (compound 18) has highly inhibitory activity against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with MIC of 0.098 μg/ml, and low cytotoxicity in normal cells. Anti-MRSA agent 3 has relatively strong ability to destroy bacterial cell wall and membrane, high binding affinity to bacterial genomic DNA .
|
-
-
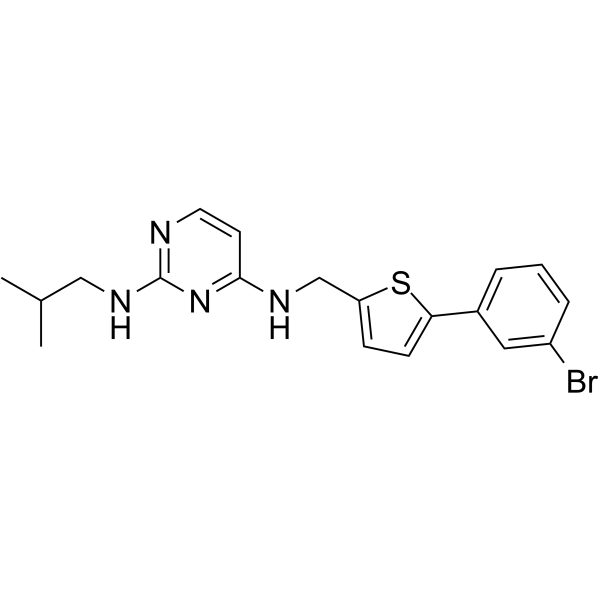
- HY-144822
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
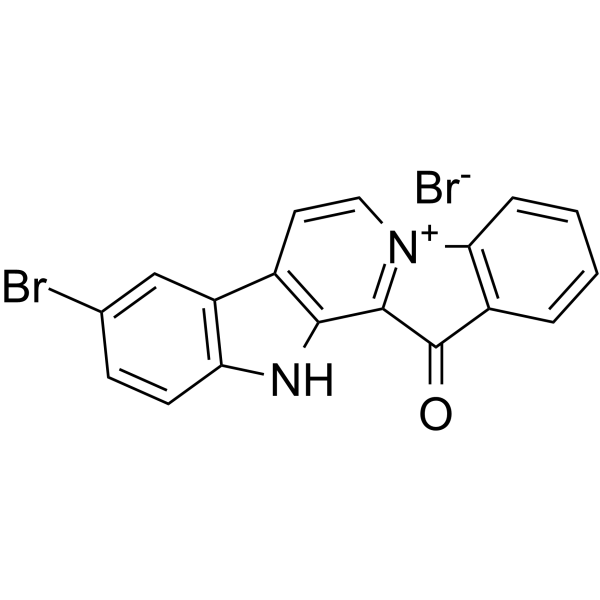
Anti-MRSA agent 2 (compound 14) has highly inhibitory activity against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with MIC of 0.098 μg/ml, and relatively low cytotoxicity in normal cells. Anti-MRSA agent 2 has strong ability to destroy bacterial membrane and bind to genomic DNA .
|
-
-
- HY-P5680
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
SpHistin is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP). SpHistin can bind to LPS (HY-D1056) and permeabilize the bacterial membrane. SpHistin combined with Rifampicin (HY-B0272) and Azithromycin (HY-17506) promotes the intracellular uptake of the antibiotics and subsequently enhances the bactericidal activity of both agents against P. aeruginosa .
|
-
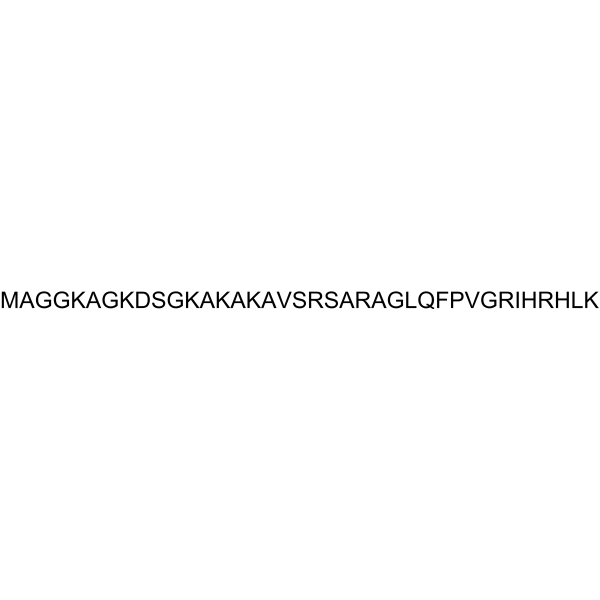
-
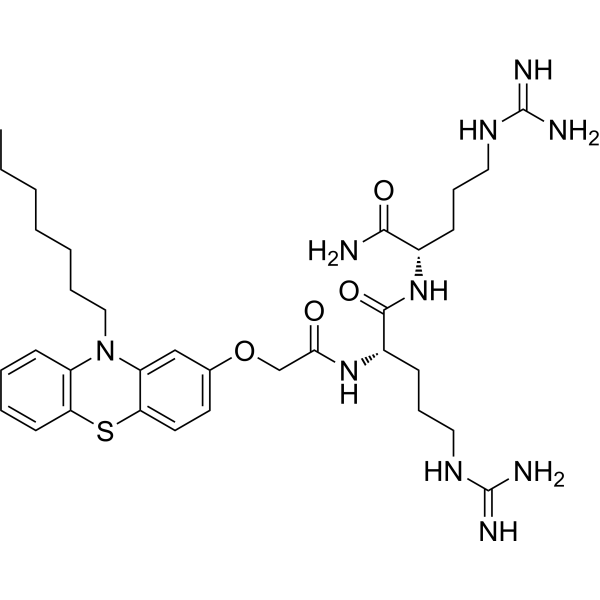
- HY-149734
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
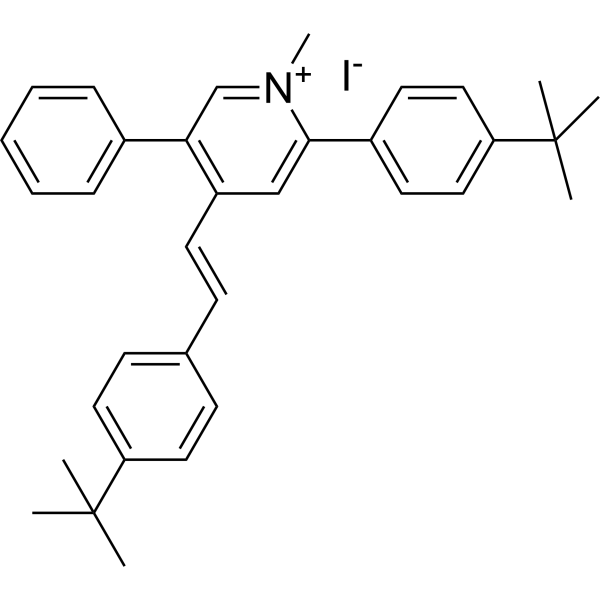
MA220607 is an antibacterial agent with low hemolytic toxicity and a dual-target mechanism of action (MOA). MA220607 promotes FtsZ protein polymerization, also increases the permeability of bacterial membranes and inhibits biofilm formation. The resistance rate of MA220607 is low, and the MICs against Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria are Table 0.062-2 μg/mL and 0.5-4 μg/mL, respectively) .
|
-
-
- HY-147546
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 107 (compound 14) is a potent antibacterial agent. Antibacterial agent 107 shows potent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, with a MIC of 1.56 μg/mL (MRSA). Antibacterial agent 107 exhibits low hemolytic activity, high membrane selectivity, and rapid bactericidal activity. Antibacterial agent 107 shows effective in vivo efficacy in the murine model of bacterial keratitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus ATCC29213 .
|
-
-
- HY-W154333
-
|
|
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
H-Arg-OtBu (dihydrochloride) is a membrane-targeting antimicrobial. H-Arg-OtBu (dihydrochloride) targets the negatively charged bacterial membrane via a combination of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. H-Arg-OtBu (dihydrochloride) can be used for bacterial infections diseases research .
|
-
-
- HY-143643
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 72 displays the antibacterial activities by targeting the bacterial membrane.
|
-
-
- HY-156005
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Others
|
|
Antibacterial agent 153 is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Antibacterial agent 153 kills bacteria by acting on the bacterial cell membrane. Antibacterial agent 153 can be used for bacterial infections research .
|
-
-
- HY-P5932
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Maculatin 1.1 TFA is an antimicrobial peptide with an MIC against Staphylococcus aureus of 7 μM. Maculatin 1.1 TFA can perforate the bacterial membrane of Staphylococcus aureus, causing bacterial death .
|
-
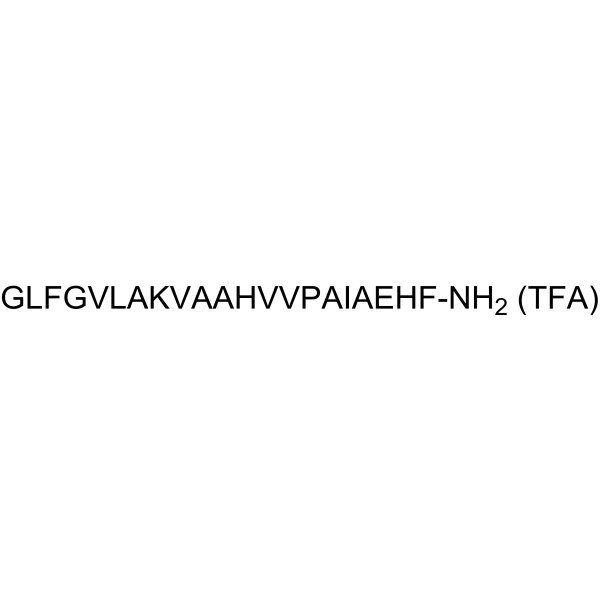
-
- HY-P5949
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
AMPR-22 is an antimicrobial peptide. AMPR-22 can bind to the bacterial membrane and induces membrane permeabilization. AMPR-22 is effective against murine model of sepsis induced by MDR strains
|
-
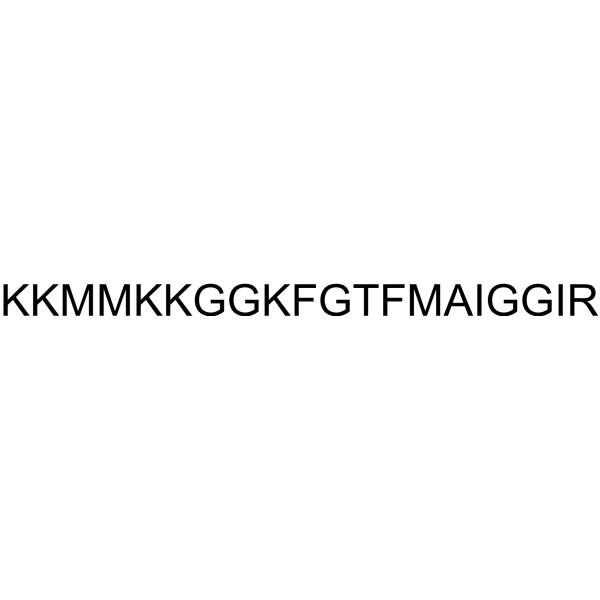
-
- HY-P3328
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MDP1, a Melittin-derived peptide, alters the integrity of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial membranes and kills the bacteria via membrane damages. MDP1 has a high-antibacterial activity against multidrug resistant (MDR) and reference strains of S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa .
|
-

-
- HY-P3328A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MDP1 acetate, a Melittin-derived peptide, alters the integrity of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial membranes and kills the bacteria via membrane damages. MDP1 acetate has a high-antibacterial activity against multidrug resistant (MDR) and reference strains of S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa .
|
-
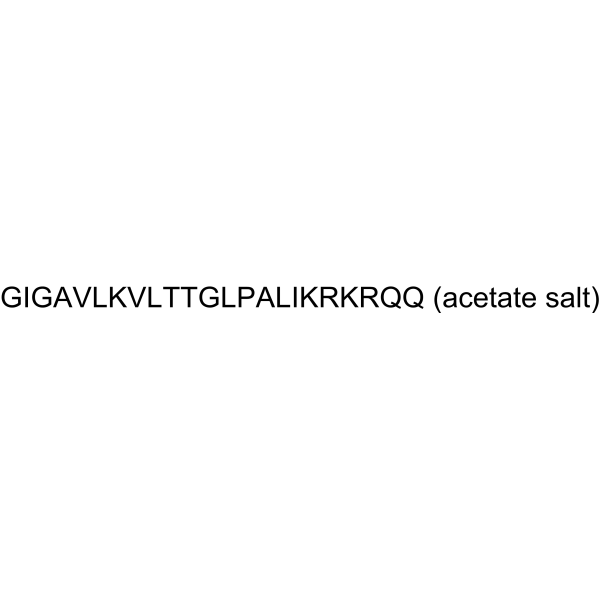
-
- HY-17362
-
|
|
Bacterial
Autophagy
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
Vancomycin hydrochloride is an antibiotic for the treatment of bacterial infections. It acts by inhibiting the second stage of cell wall synthesis of susceptible bacteria. Vancomycin also alters the permeability of the cell membrane and selectively inhibits ribonucleic acid synthesis.
|
-
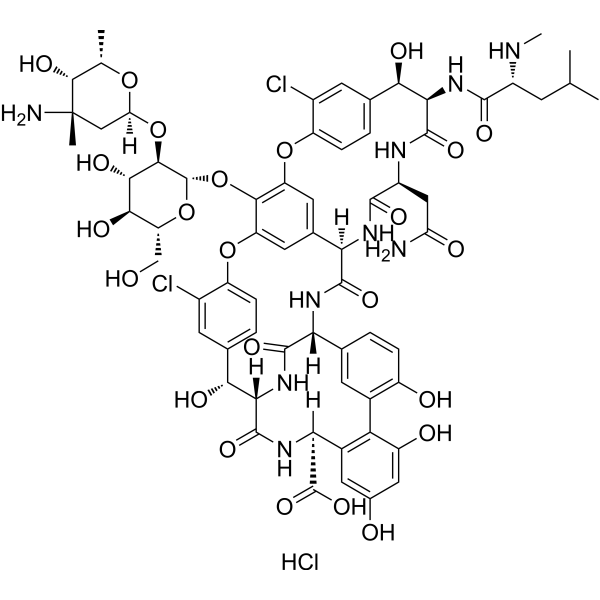
-
- HY-P0311
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LAH4, an alpha-helix of the designed amphipathic peptide antibiotic, exhibits potent antimicrobial, nucleic acid transfection and cell penetration activities. LAH4 possesses high plasmid DNA delivery capacities. LAH4 has a strong affinity for anionic lipids found in the outer membrane of bacterial membranes .
|
-
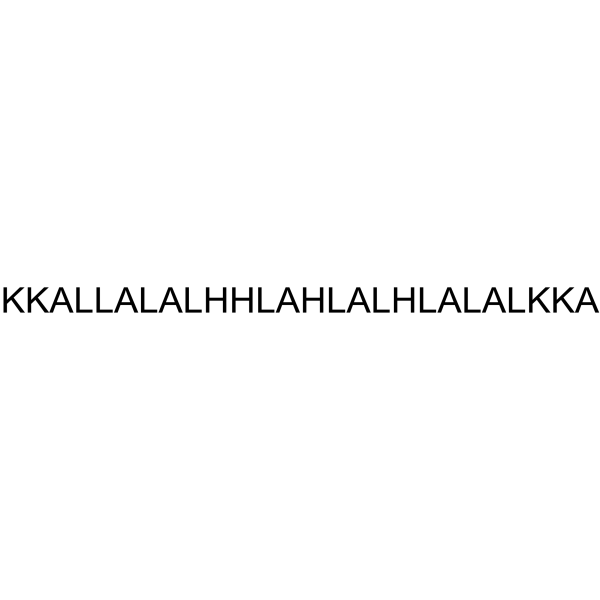
-
- HY-W013699
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
Cancer
|
|
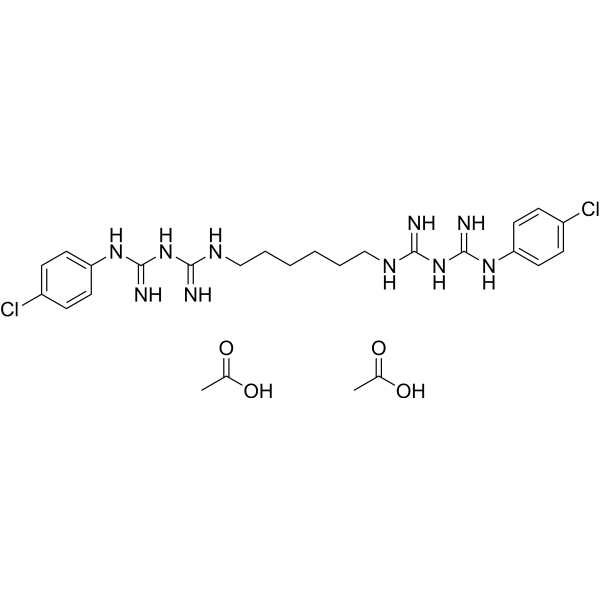
Chlorhexidine diacetate is a biguanide disinfectant with rapid bactericidal activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative organism. The antibacterial effect of chlorhexidine diacetate is related to its action on the bacterial cell membrane and to precipitation of intracellular contents .
|
-
-
- HY-P0311A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LAH4 TFA, an alpha-helix of the designed amphipathic peptide antibiotic, exhibits potent antimicrobial, nucleic acid transfection and cell penetration activities. LAH4 TFA possesses high plasmid DNA delivery capacities. LAH4 TFA has a strong affinity for anionic lipids found in the outer membrane of bacterial membranes .
|
-
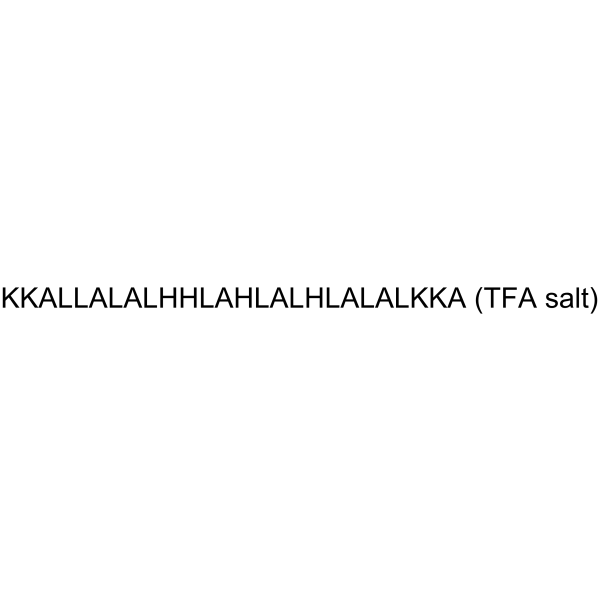
-
- HY-A0248A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Polymyxin B1 is a potent antimicrobial lipopeptide first derived from Bacilus polymyxa. Polymyxin B1 is the major component in Polymyxin B (HY-A0248). Polymyxin B1 can induce lysis of bacterial cells through interaction with their membranes. Polymyxin B1 has the potential for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections treatment .
|
-
-
- HY-149095
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 139 has antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria. Antibacterial agent 139 has anti-MRSA, anti-VISA, and anti-LRSE activities. Antibacterial agent 139 depolarizes the bacterial cell membrane .
|
-
-
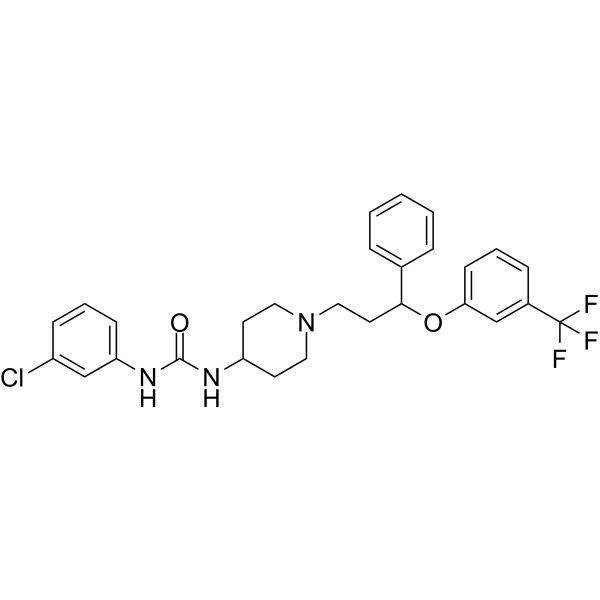
- HY-149353
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 145 (compound 1b) is an antibacterial agent depending on bacterial iron uptake pathway. Antibacterial agent 145 disrupts cytoplasmic membrane integrity and inhibits cell metabolism but exhibits low cytotoxic effects to normal cells .
|
-
-
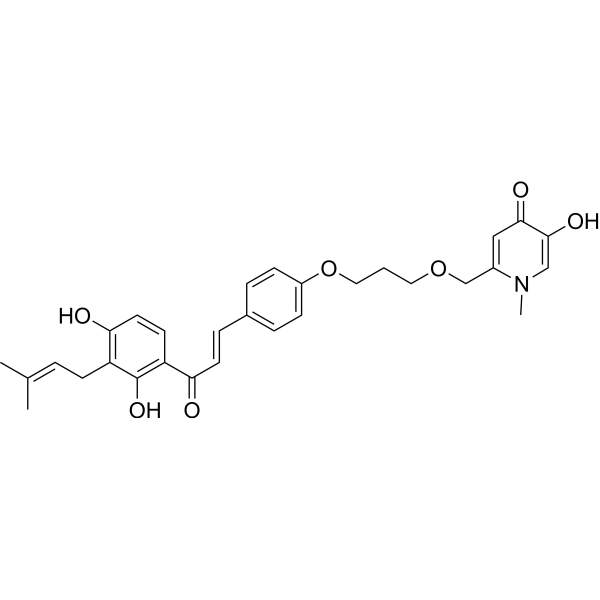
- HY-P5553
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
cPcAMP1/26 is an antimicrobial peptide. cPcAMP1/26 effectively kills A.hydrophila and S. aureus. cPcAMP1/26 induces depolarization of the bacterial plasma membrane, and increases intracellular ROS levels .
|
-
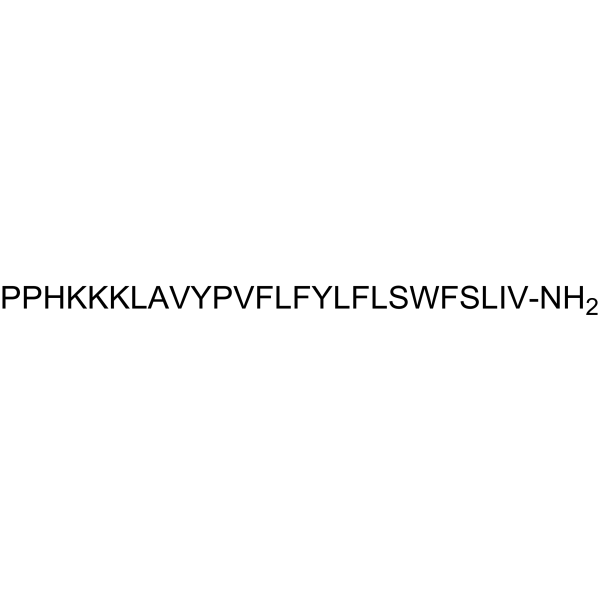
-
- HY-P5712
-
|
Gramicidin soviet
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Gramicidin S (Gramicidin soviet) is a cationic cyclic peptide antibiotic. Gramicidin S is active against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria by perturbing integrity of the bacterial membranes. Gramicidin S also inhibits cytochrome bd quinol oxidase .
|
-
-
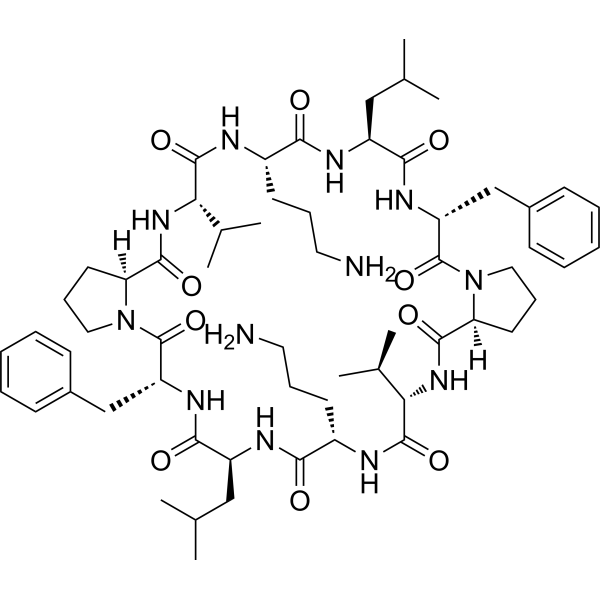
- HY-162451
-
|
|
Bacterial
Reactive Oxygen Species
Glucosidase
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 207 (Compound Ru1) has antibacterial activity against S. aureus (MIC: 1 μg/mL), and low resistance frequencies. Antibacterial agent 207 destroys the bacterial cell membrane, promote production of ROS in bacteria .
|
-
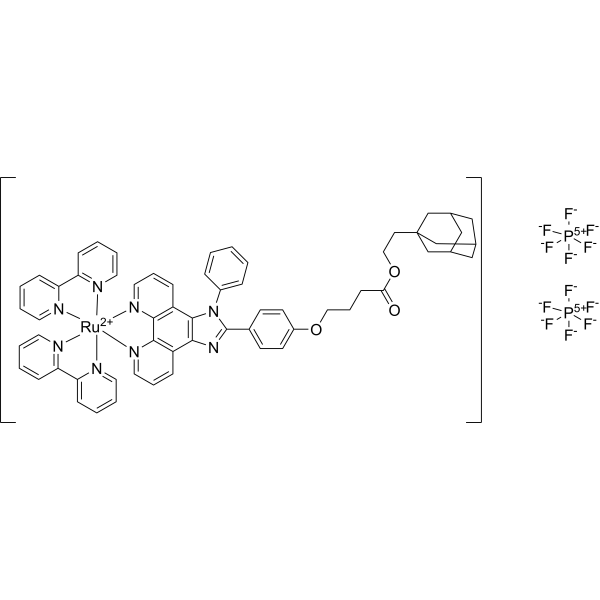
-
- HY-161404
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 202 (compound 45c) is a low cytotoxic bacterial inhibitor with good activity against Gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, especially Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration)=7.8-31.25 μM). Antibacterial agent 202 can exert antibacterial activity by destroying the integrity of cell membranes and can be used in the research of bacterial infections .
|
-
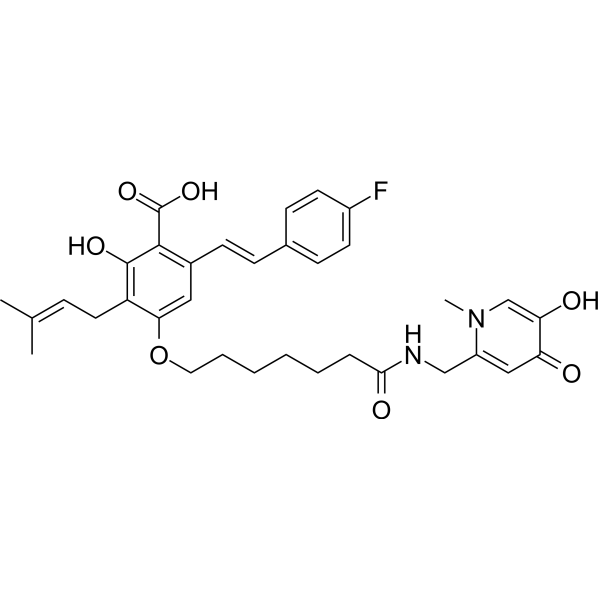
-
- HY-P2460
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
SMAP-29, a promising antiinfective agent, is a broad spectrum antibacterial and antifungal α-helical cathelicidin-derived peptide. SMAP-29 acts by permeabilizing bacterial membranes and inducing remarkable changes in the surface morphology of susceptible microorganism .
|
-
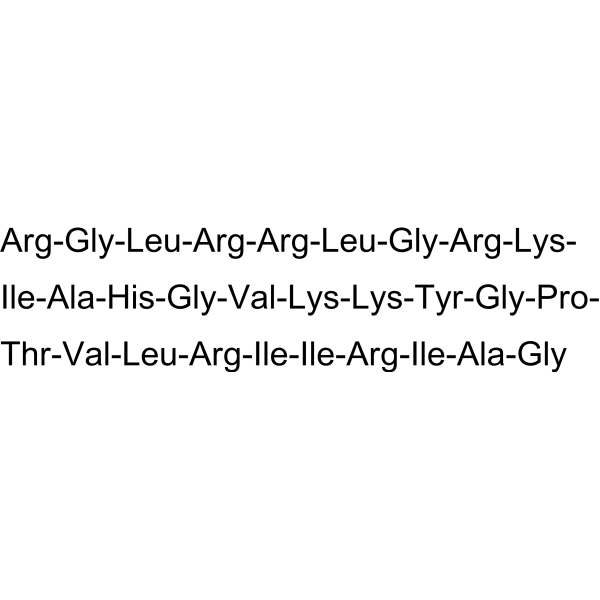
-
- HY-149810
-
|
|
Bacterial
Parasite
|
Infection
|
|
AcrB-IN-2 is an AcrB efflux pump inhibitor, with ability to potentiate the effect of antibiotics. AcrB-IN-22 inhibits Nile Red (a known substrate of AcrB) efflux.AcrB-IN-2 does not disrupts the bacterial outer membrane nor display toxicity in a nematode model .
|
-
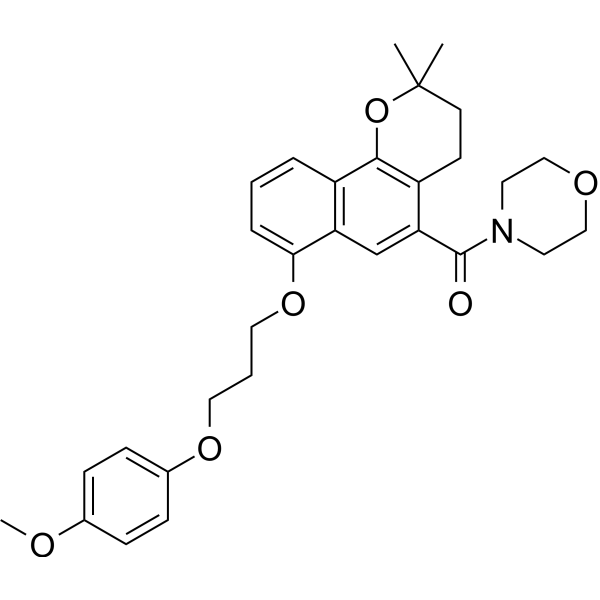
-
- HY-146047
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Antibacterial agent 94 (compound 5b) is a potent antibacterial agent. Antibacterial agent 94 show antibacterial activities and show the capability of eradicating MRSA persisters. Antibacterial agent 94 has an effect on bacterial membrane. Antibacterial agent 94 interferes in phosphatidylglycerol (PG) synthesis pathway .
|
-
-
- HY-156289
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
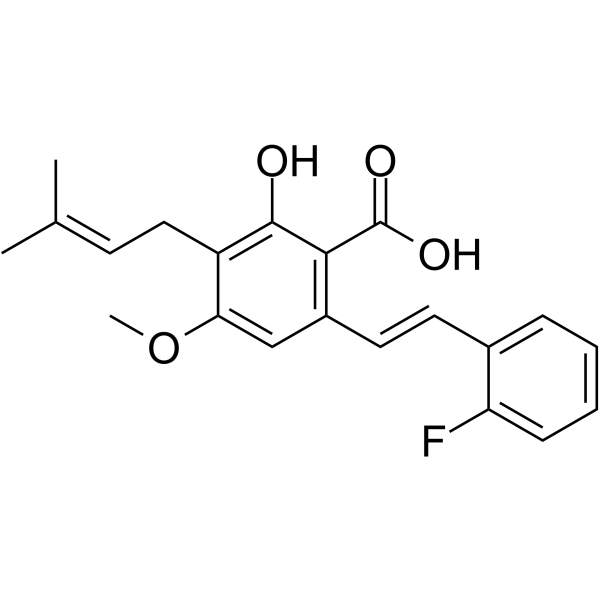
Anti-MRSA agent 8 (Compound 7g) is a DAPG derivative with strong antibacterial activity. Anti-MRSA agent 8 assertes its activity by targeting bacterial cell membranes. Anti-MRSA agent 8 can be used for the research of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) .
|
-
-
- HY-149811
-
|
|
Bacterial
Parasite
|
Infection
|
|
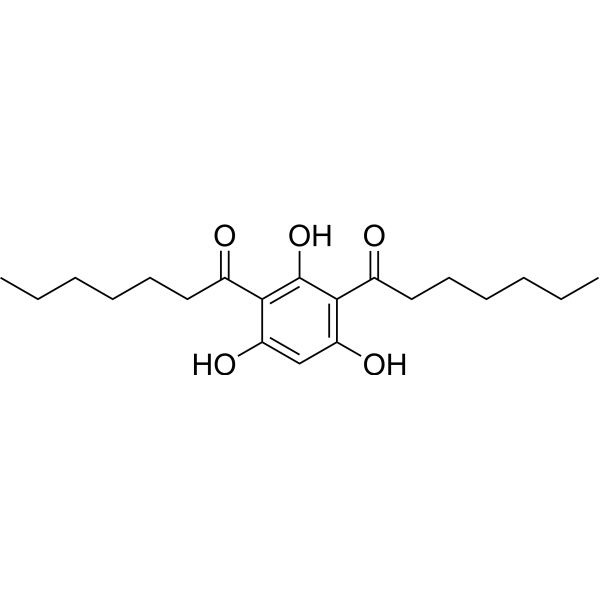
Efflux pump-IN-3 is an AcrB efflux pump inhibitor, with ability to potentiate the effect of antibiotics. Efflux pump-IN-3 inhibits Nile Red (a known substrate of AcrB) efflux. Efflux pump-IN-3 does not disrupts the bacterial outer membrane nor display toxicity in a nematode model .
|
-
-
- HY-149812
-
|
|
Bacterial
Parasite
|
Infection
|
|
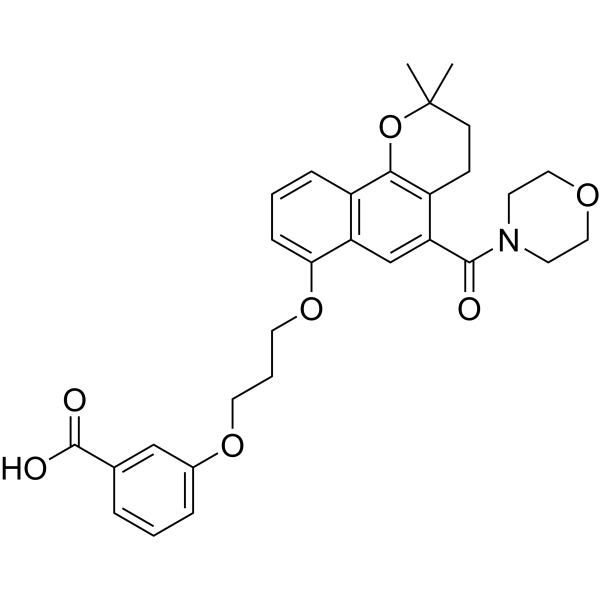
Efflux pump-IN-4 is an AcrB efflux pump inhibitor, with ability to potentiate the effect of antibiotics. Efflux pump-IN-4 inhibits Nile Red (a known substrate of AcrB) efflux. Efflux pump-IN-4 does not disrupts the bacterial outer membrane nor display toxicity in a nematode model .
|
-
-
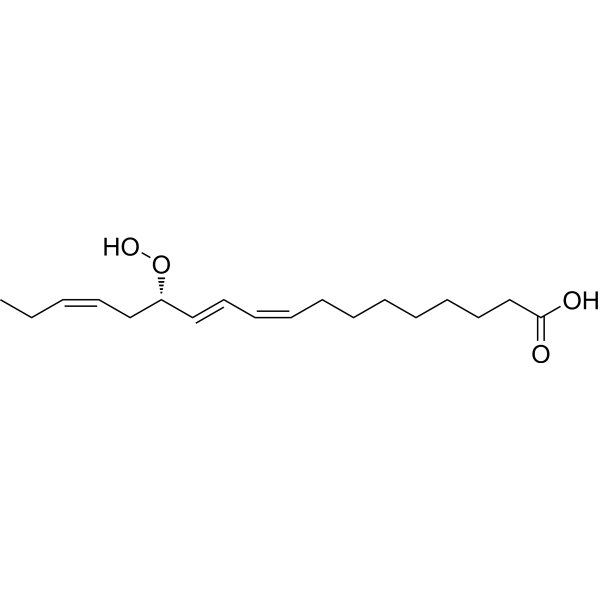
- HY-130323
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
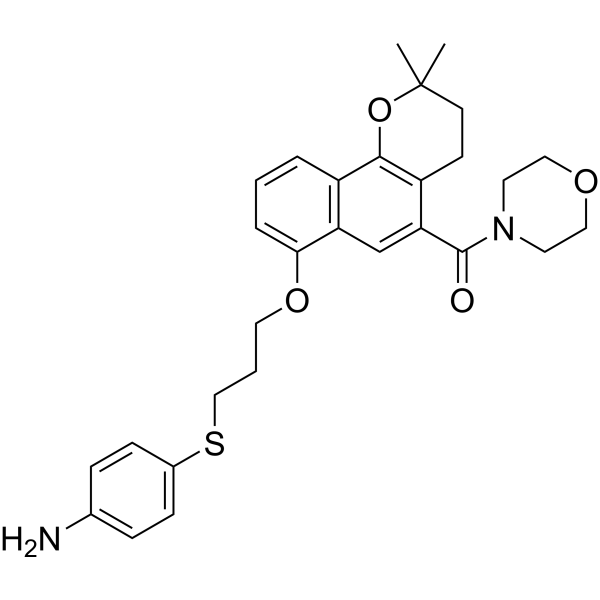
13-HPOT, a linolenic fatty acid hydroperoxide, is an antibacterial agent. 13-HPOT has a strong dose response effect on three plant pathogen gram negative bacteria: Pectobacterium carotovorum, Pseudomonas syringae and Xanthomonas translucens. 13-HPOT can interact with the lipid representative of the inner bacterial plasma membrane .
|
-
-
- HY-P5203
-
|
EntK1
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Enterocin K1 (EntK1) is a bacteriocin. Enterocin K1 is a ribosomal synthetic peptide. Enterocin K1 specifically targets Enterococcus faecalis via the Eep protein on the bacterial membrane. Enterocin K1 displays a potent antibacterial activity against VRE. Enterocin K1 can be used for related studies of VRE infections .
|
-

-
- HY-135416
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Infection
|
|
Streptolysin O, a group A streptococcal toxin, is a well-characterized oxygen-labile prototype of a cholesterol-binding bacterial exotoxin. Streptolysin O causes both lysis of cells and cardiotoxicity. Streptolysin O is widely used for the controlled permeabilization of cell membranes. Streptolysin O exists in two forms, a reduced active state and an oxidized reversibly inactive state .
|
-
-
- HY-112959
-
|
TD-6424
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
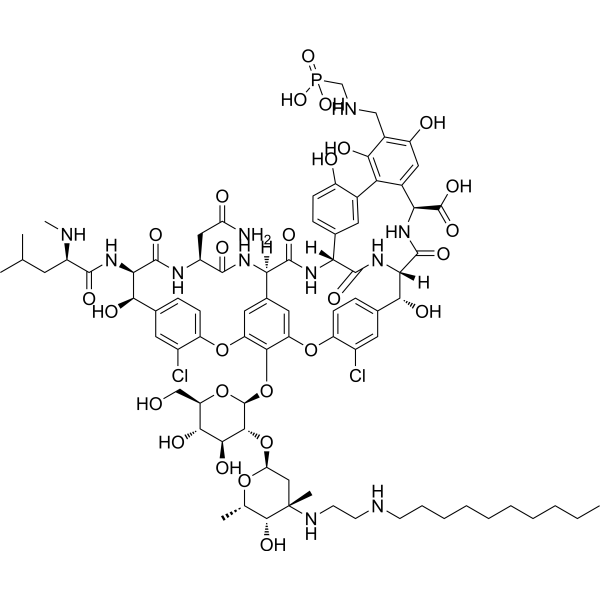
Telavancin (TD-6424) is a semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide vancomycin-derivative, is a novel antimicrobial agent developed by Theravance for overcoming resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections, specifically methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Telavancin disrupts cell membrane integrity, can be used for research of complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSIs) caused by Gram-positive bacteria .
|
-
-
- HY-129555
-
|
|
Bacterial
HSV
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
Surfactin is a potent cyclic lipopeptide biosurfactants consists of four isomers (Surfactin A, B, C and D), which mediates flux of mono-and divalent cations, such as calcium, across lipid bilayer membranes. Surfactin can act as an antimicrobial adjuvant with anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, antimycoplasma and hemolytic effects . Surfactin also has antiviral activity against a variety of enveloped viruses .
|
-

-
- HY-128780B
-
|
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
|
Infection
|
|
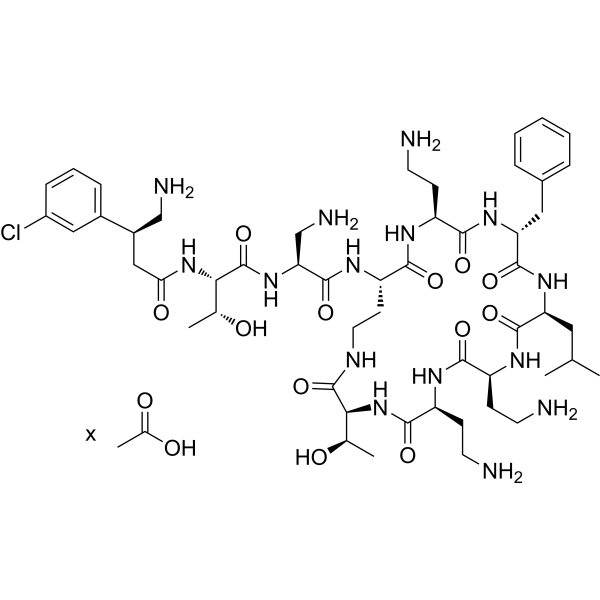
SPR206 acetate is a polymyxin analog with antibiotic activity against Gram-negative pathogens, including multidrug-resistant (MDR) variants. SPR206 acetate has an anti-bacterial infection effect by interacting with the bacterium’s outer membrane. The MIC values of SPR206 acetate against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pa14 and Acinetobacter baumannii NCTC13301 are both 0.125 mg/L .
|
-
-
- HY-147181
-
|
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
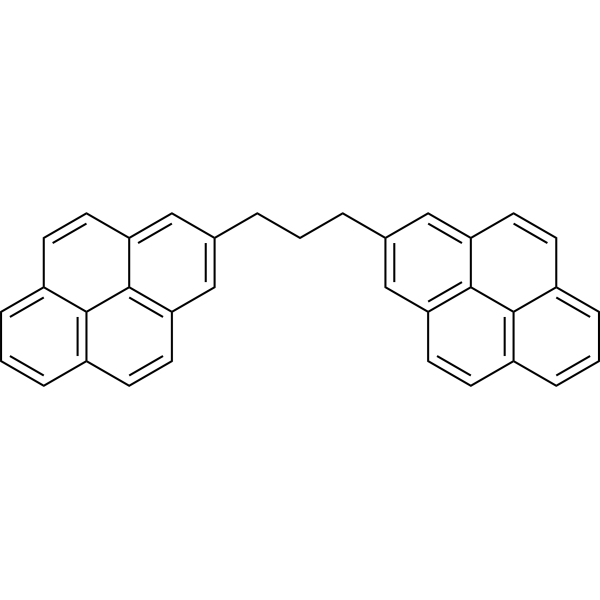
1,3-Di-(2-pyrenyl)propane is a fluorescent indicator. 1,3-Di-(2-pyrenyl)propane can be used in fluidity of bacterial membrane lipids monitored by intramolecular excimerization. 1,3-Di-(2-pyrenyl)propane shows temperature dependence of fluorescence lifetime distributions .
|
-
-
- HY-P0270
-
|
Magainin II
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Magainin 2 (Magainin II) is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) isolated from the skin of the African clawed frog Xenopus laevis. Magainin 2 displays antibiotic activity against numerous gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Magainin 2 also is active against protozoa . Magainin 2 exerts its cytotoxicity effects by preferential interactions with anionic phospholipids abundant in bacterial membranes .
|
-
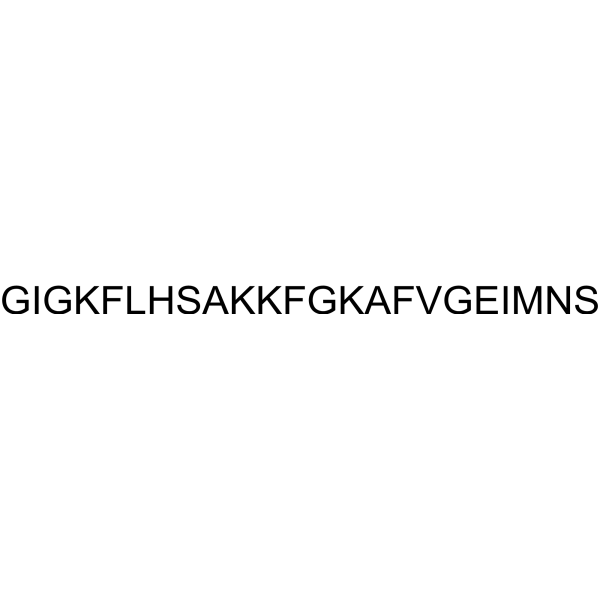
-
- HY-118540
-
|
Diazoresorcinol
|
Fluorescent Dye
|
Others
|
|
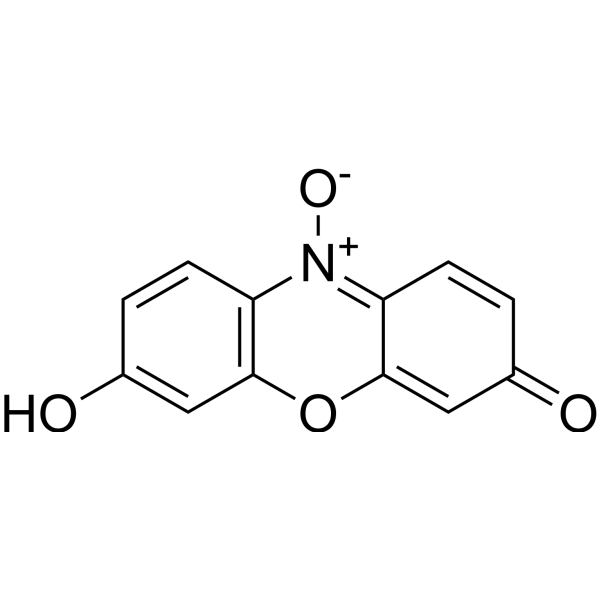
Resazurin (Diazoresorcinol) is a water-soluble, non-toxic, stable, membrane-permeable blue non-fluorescent dye (faintly fluorescent). Resazurin is used as a redox indicator, can be reduced to pink, highly fluorescent Resorufin (Ex=530-560 nm, Em=590 nm) in living cells. Resazurin can be used for the detection of cell viability, toxicity, proliferation, migration and invasion in cells (human, plant and animal, bacterial and fungal) .
|
-
-
- HY-146460
-
|
|
Reactive Oxygen Species
|
Infection
|
|
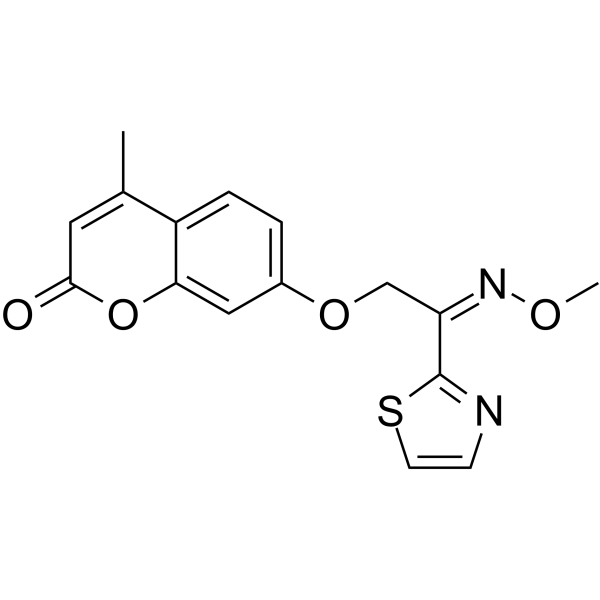
Antimicrobial agent-2 (compound V-a) is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent, possessing inhibitory activity against various Gram-positive and -negative bacteria. Antimicrobial agent-2 has excellent inhibitory effect on Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) with a MIC of 1 μg/mL. Antimicrobial agent-2 can effectively damage the membrane and lead to the leakage of protein, also can induce the generation of ROS. Antimicrobial agent-2 exhibits low toxicity, no obvious resistance and good bioavailability .
|
-
-
- HY-135416A
-
|
|
Endogenous Metabolite
|
Infection
|
|
Streptolysin O (≥1000000 units/mg) is a ≥1000000 units/mg Streptolysin O (HY-135416). Streptolysin O, a group A streptococcal toxin, is a well-characterized oxygen-labile prototype of a cholesterol-binding bacterial exotoxin. Streptolysin O causes both lysis of cells and cardiotoxicity. Streptolysin O is widely used for the controlled permeabilization of cell membranes. Streptolysin O exists in two forms, a reduced active state and an oxidized reversibly inactive state .
|
-
-
- HY-P5601
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
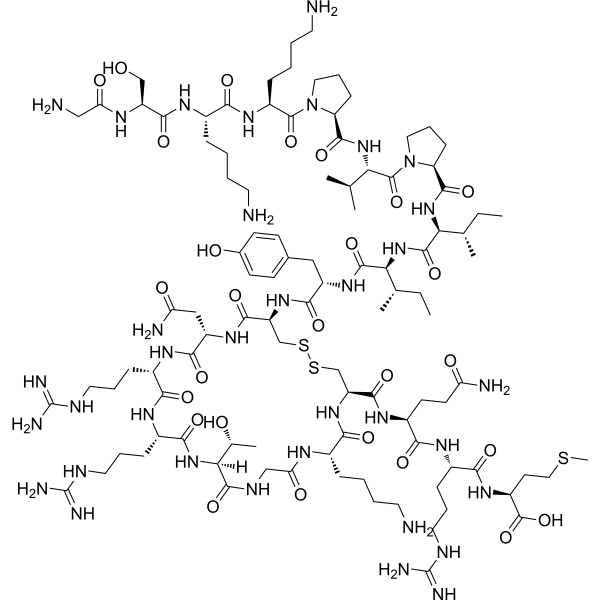
Thanatin is an inducible cationic antimicrobial peptide. Thanatin is a pathogen-inducible single-disulfide-bond-containing β-hairpin AMP. Thanatin displays broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as against various species of fungi with MICs of 0.3-40 µM, 0.6-40 µM and 0.6-20 µM, respectively. Thanatin has the property of competitive replacement of divalent cations from bacterial outer membrane (OM), leading to OM disruption .
|
-
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
-
-
- HY-P5601A
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
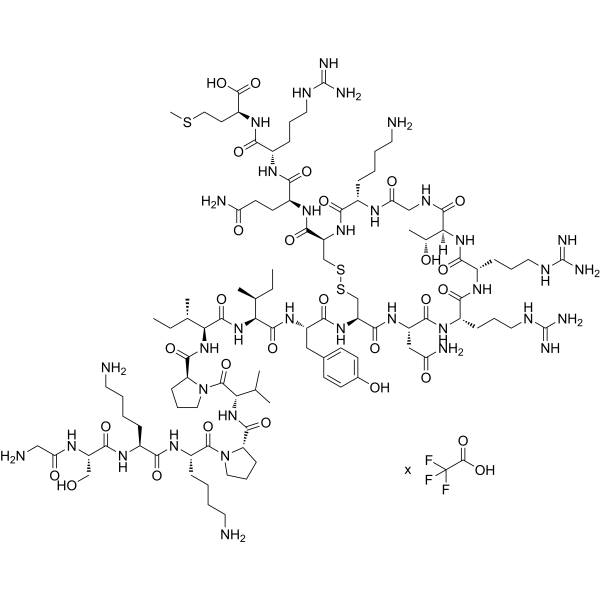
Thanatin TFA is an inducible cationic antimicrobial peptide. Thanatin TFA s a pathogen-inducible single-disulfide-bond-containing β-hairpin AMP. Thanatin TFA displays broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as against various species of fungi with MICs of 0.3-40 µM, 0.6-40 µM and 0.6-20 µM, respectively. Thanatin TFA has the property of competitive replacement of divalent cations from bacterial outer membrane (OM), leading to OM disruption .
|
-
-
- HY-W251428
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
Others
|
|
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid that is a component of plant, animal and bacterial cell membranes. It is present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes less than phosphatidylethanolamine, and in eukaryotes less than phosphatidylcholine. It is formed by the reaction between CDP-diglyceride and L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is the metabolic precursor of cardiolipin. Phosphatidylglycerols containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote the proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively. Phosphatidylglycerol is the second-largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, accounting for 10% of lipids, and has reduced levels of pulmonary surfactant in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Phosphatidylglycerol (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from eggs with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. References: [1]. Ohtsuka, T., Nishijima, M., and Akamatsu, Y. Phosphatidylglycerol phosphate synthase-deficient somatic mutants with impaired phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin biosynthesis J. Biol. Chemical. 268(30), 22908-22913 (1993).[2]. Furse, S. Are phosphatidylglycerols essential for terrestrial life J. Chemistry. biology. 10(1), 1-9 (2016).[3]. Xie, D., Seremwe, M., Edwards, JG, et al. Different effects of different phosphatidylglycerols on the proliferation of mouse keratinocytes PLoS One 9(9), e107119 (2014).
|
-

-
-
HY-L067
-
|
|
633 compounds
|
|
Antibiotics are types of antimicrobial products used for the treatment and prevention of bacterial infections. Antibiotics can kill or inhibit bacterial growth. Although the target of an antibiotic is bacteria, some antibiotics also attack fungi and protozoans. However, antibiotics rarely have an effect on viruses. The major mechanism underlying antibiotics is the inhibition or regulation of enzymes involved in cell wall biosynthesis, nucleic acid metabolism and repair, protein synthesis, or disruption of membrane structure. Many of these cellular functions targeted by antibiotics are most active in multiplying cells. Since there is often overlap in these functions between prokaryotic bacterial cells and eukaryotic mammalian cells, it is not surprising that some antibiotics have also been found to be useful as anticancer agents.
MCE supplies a unique collection of 633 antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides, etc. MCE Antibiotics Library is a useful tool for anti-bacterial or anti-cancer drugs discovery.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-118540
-
|
Diazoresorcinol
|
Fluorescent Dyes/Probes
|
|
Resazurin (Diazoresorcinol) is a water-soluble, non-toxic, stable, membrane-permeable blue non-fluorescent dye (faintly fluorescent). Resazurin is used as a redox indicator, can be reduced to pink, highly fluorescent Resorufin (Ex=530-560 nm, Em=590 nm) in living cells. Resazurin can be used for the detection of cell viability, toxicity, proliferation, migration and invasion in cells (human, plant and animal, bacterial and fungal) .
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Type |
-
- HY-W251428
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid that is a component of plant, animal and bacterial cell membranes. It is present in prokaryotes and eukaryotes less than phosphatidylethanolamine, and in eukaryotes less than phosphatidylcholine. It is formed by the reaction between CDP-diglyceride and L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is the metabolic precursor of cardiolipin. Phosphatidylglycerols containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote the proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively. Phosphatidylglycerol is the second-largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, accounting for 10% of lipids, and has reduced levels of pulmonary surfactant in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Phosphatidylglycerol (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from eggs with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. References: [1]. Ohtsuka, T., Nishijima, M., and Akamatsu, Y. Phosphatidylglycerol phosphate synthase-deficient somatic mutants with impaired phosphatidylglycerol and cardiolipin biosynthesis J. Biol. Chemical. 268(30), 22908-22913 (1993).[2]. Furse, S. Are phosphatidylglycerols essential for terrestrial life J. Chemistry. biology. 10(1), 1-9 (2016).[3]. Xie, D., Seremwe, M., Edwards, JG, et al. Different effects of different phosphatidylglycerols on the proliferation of mouse keratinocytes PLoS One 9(9), e107119 (2014).
|
-
- HY-142991
-
|
POPG
|
Drug Delivery
|
|
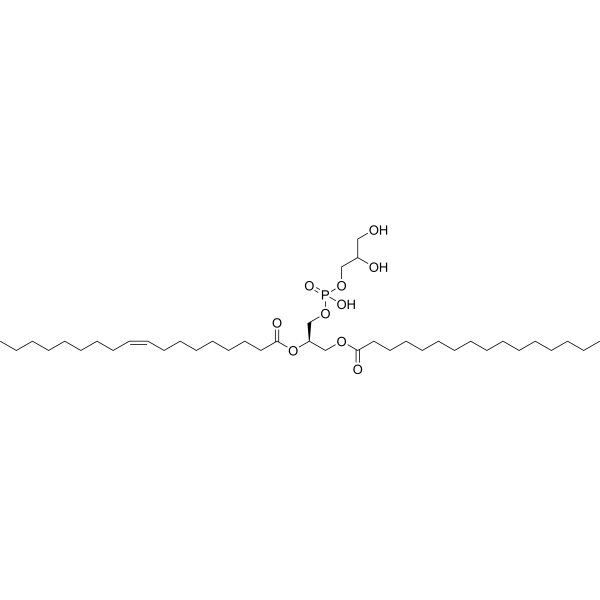
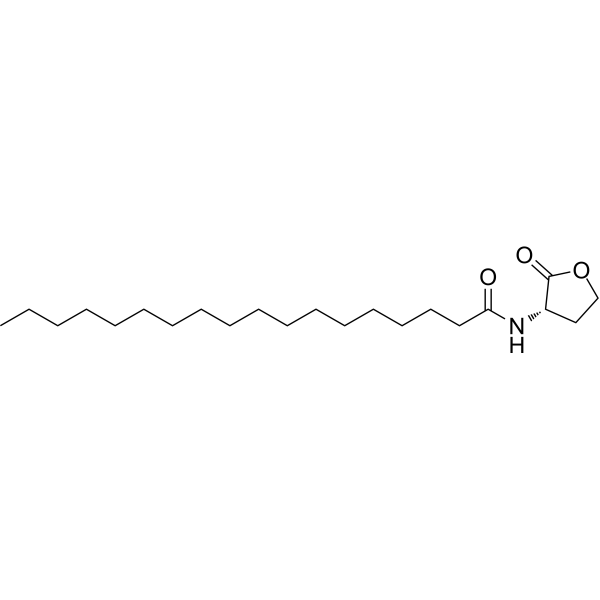
1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylglycerol (POPG) can be used to formulate bacterial membrane mimetic .
|
-
- HY-W127487
-
|
|
Biochemical Assay Reagents
|
|
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria to control gene expression in response to increased cell density. This regulatory process manifests itself in a variety of phenotypes, including biofilm formation and virulence factor production. Coordinated gene expression is achieved through the production, release and detection of small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers. N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise a class of such autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled to a homoserine lactone (HSL). Modulation of bacterial quorum-sensing signaling systems to suppress pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial research for infectious diseases. AHLs differ in acyl length (C4-C18), C3 substitution (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signaling specificity through the affinity of the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. C18-HSL, one of four lipophilic long acyl side chain AHLs produced by the LuxI AHL synthase homolog SinI, is involved in quorum-sensing signaling in strains of Rhizobium meliloti (a nitrogen-fixing bacterial symbiont of the legume M. sativa) . C18-HSL and other hydrophobic AHLs tend to localize in the relatively lipophilic environment of bacterial cells and cannot diffuse freely across the cell membrane. Long-chain N-acyl homoserine lactones can be exported from cells by efflux pumps, or can be transported between communicating cells by extracellular outer membrane vesicles.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Target |
Research Area |
-
- HY-P5932
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Maculatin 1.1 TFA is an antimicrobial peptide with an MIC against Staphylococcus aureus of 7 μM. Maculatin 1.1 TFA can perforate the bacterial membrane of Staphylococcus aureus, causing bacterial death .
|
-
- HY-P3328A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MDP1 acetate, a Melittin-derived peptide, alters the integrity of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial membranes and kills the bacteria via membrane damages. MDP1 acetate has a high-antibacterial activity against multidrug resistant (MDR) and reference strains of S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa .
|
-
- HY-P5680
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
SpHistin is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP). SpHistin can bind to LPS (HY-D1056) and permeabilize the bacterial membrane. SpHistin combined with Rifampicin (HY-B0272) and Azithromycin (HY-17506) promotes the intracellular uptake of the antibiotics and subsequently enhances the bactericidal activity of both agents against P. aeruginosa .
|
-
- HY-P5949
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
AMPR-22 is an antimicrobial peptide. AMPR-22 can bind to the bacterial membrane and induces membrane permeabilization. AMPR-22 is effective against murine model of sepsis induced by MDR strains
|
-
- HY-P3328
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
MDP1, a Melittin-derived peptide, alters the integrity of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial membranes and kills the bacteria via membrane damages. MDP1 has a high-antibacterial activity against multidrug resistant (MDR) and reference strains of S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa .
|
-
- HY-P0311
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LAH4, an alpha-helix of the designed amphipathic peptide antibiotic, exhibits potent antimicrobial, nucleic acid transfection and cell penetration activities. LAH4 possesses high plasmid DNA delivery capacities. LAH4 has a strong affinity for anionic lipids found in the outer membrane of bacterial membranes .
|
-
- HY-P0311A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
LAH4 TFA, an alpha-helix of the designed amphipathic peptide antibiotic, exhibits potent antimicrobial, nucleic acid transfection and cell penetration activities. LAH4 TFA possesses high plasmid DNA delivery capacities. LAH4 TFA has a strong affinity for anionic lipids found in the outer membrane of bacterial membranes .
|
-
- HY-A0248A
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Polymyxin B1 is a potent antimicrobial lipopeptide first derived from Bacilus polymyxa. Polymyxin B1 is the major component in Polymyxin B (HY-A0248). Polymyxin B1 can induce lysis of bacterial cells through interaction with their membranes. Polymyxin B1 has the potential for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections treatment .
|
-
- HY-P5553
-
|
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
cPcAMP1/26 is an antimicrobial peptide. cPcAMP1/26 effectively kills A.hydrophila and S. aureus. cPcAMP1/26 induces depolarization of the bacterial plasma membrane, and increases intracellular ROS levels .
|
-
- HY-P5712
-
|
Gramicidin soviet
|
Antibiotic
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Gramicidin S (Gramicidin soviet) is a cationic cyclic peptide antibiotic. Gramicidin S is active against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria by perturbing integrity of the bacterial membranes. Gramicidin S also inhibits cytochrome bd quinol oxidase .
|
-
- HY-P2460
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
Inflammation/Immunology
|
|
SMAP-29, a promising antiinfective agent, is a broad spectrum antibacterial and antifungal α-helical cathelicidin-derived peptide. SMAP-29 acts by permeabilizing bacterial membranes and inducing remarkable changes in the surface morphology of susceptible microorganism .
|
-
- HY-P5203
-
|
EntK1
|
Bacterial
|
Infection
|
|
Enterocin K1 (EntK1) is a bacteriocin. Enterocin K1 is a ribosomal synthetic peptide. Enterocin K1 specifically targets Enterococcus faecalis via the Eep protein on the bacterial membrane. Enterocin K1 displays a potent antibacterial activity against VRE. Enterocin K1 can be used for related studies of VRE infections .
|
-
- HY-P0270
-
|
Magainin II
|
Bacterial
Antibiotic
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Magainin 2 (Magainin II) is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) isolated from the skin of the African clawed frog Xenopus laevis. Magainin 2 displays antibiotic activity against numerous gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Magainin 2 also is active against protozoa . Magainin 2 exerts its cytotoxicity effects by preferential interactions with anionic phospholipids abundant in bacterial membranes .
|
-
- HY-P5601
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Thanatin is an inducible cationic antimicrobial peptide. Thanatin is a pathogen-inducible single-disulfide-bond-containing β-hairpin AMP. Thanatin displays broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as against various species of fungi with MICs of 0.3-40 µM, 0.6-40 µM and 0.6-20 µM, respectively. Thanatin has the property of competitive replacement of divalent cations from bacterial outer membrane (OM), leading to OM disruption .
|
-
- HY-P5601A
-
|
|
Bacterial
Fungal
|
Infection
|
|
Thanatin TFA is an inducible cationic antimicrobial peptide. Thanatin TFA s a pathogen-inducible single-disulfide-bond-containing β-hairpin AMP. Thanatin TFA displays broad-spectrum activity against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as against various species of fungi with MICs of 0.3-40 µM, 0.6-40 µM and 0.6-20 µM, respectively. Thanatin TFA has the property of competitive replacement of divalent cations from bacterial outer membrane (OM), leading to OM disruption .
|
-
- HY-K1044
-
|
|
|
Polymixin B is a mixture of B1 and B2 polypeptides obtained from different strains of Bacillus polymyxa, with antibacterial activity against gram-negative bacteria. It can bind lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and disrupts the cytoplasmic membrane by inducing large pores to allow nucleotide leakage in bacterial walls. This disrupts the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane.
|
| Cat. No. |
Product Name |
Category |
Target |
Chemical Structure |
Your information is safe with us. * Required Fields.
Inquiry Information
- Product Name:
- Cat. No.:
- Quantity:
- MCE Japan Authorized Agent: